In recent years, tinplate has been widely used in the packaging industry due to its excellent corrosion resistance, formability, and printability. From food cans to high-end gift boxes, tinplate can be found in almost every product.
So, how is this material printed? This article will provide an in-depth understanding of the entire tinplate printing process, analyzing its printing techniques and technical requirements.

What is tinplate printing?
1. How is tinplate printing different from ordinary printing?
Tinplate printing differs fundamentally from ordinary paper printing, primarily in the materials and processes used. Tinplate is an electroplated metal material with a smooth and hard surface. Printing on tinplate typically uses techniques such as offset printing and silk-screen printing, which differ from the requirements for printing on paper. Tinplate printing not only requires overcoming the adhesion challenges of the metal surface coating but also ensuring the durability of the print, gloss, and depth of color. Therefore, tinplate sheet printing requires specialized machinery and equipment, as well as specific ink materials.
2. What preparations are required before tinplate printing?
Before officially printing tinplate, preparation is crucial. First, the tinplate sheet needs to be degreased to remove surface oil and improve ink adhesion. Afterward, the tinplate undergoes a chemical treatment to increase surface roughness, allowing for better ink adhesion. Furthermore, the surface finish of the tinplate must be carefully controlled to ensure clarity and uniformity of the printed pattern. Only after these preparations are complete can the printing process begin.
What processes are used for tinplate printing?
1. How is offset printing applied to tinplate?
Offset printing is currently one of the most commonly used processes for tinplate sheet printing. It primarily uses a rubber blanket to transfer the design onto the tinplate surface. Offset printing not only achieves high-resolution printing but also produces rich color gradations. The basic principle of offset printing is to utilize the absorption and repulsion of ink to precisely transfer the design onto the tinplate using a rubber cylinder. Because the tinplate surface is smooth, the offset printing process requires specialized inks and a low-temperature curing process to prevent high temperatures from causing metal deformation or affecting the print quality.
2. Is screen printing suitable for tinplate?
Screen printing is also commonly used on tinplate, particularly for printing single-color patterns or large areas of color. The advantage of screen printing lies in its thick ink layer, which creates a more three-dimensional pattern. However, its low resolution prevents the reproduction of intricate details. Screen printing typically uses solvent-based inks, which are applied to the tinplate surface via a squeegee. Due to the thicker ink layer, screen-printed patterns produce rich colors and are highly abrasion-resistant, making them a popular choice for printing on packaging that requires durability.
3. How does UV printing improve tinplate printing?
UV printing, a printing process that uses ultraviolet light to cure inks, can significantly improve the speed and quality of tinplate sheet printing. UV inks offer extremely fast drying times, facilitating printing efficiency. They also have strong adhesion and can achieve high-gloss designs. Because UV inks do not emit solvents, they are environmentally friendly and offer excellent color reproduction. Therefore, UV printing is suitable for tinplate printing requiring high gloss and abrasion resistance, particularly for high-end packaging and exquisite gift boxes.
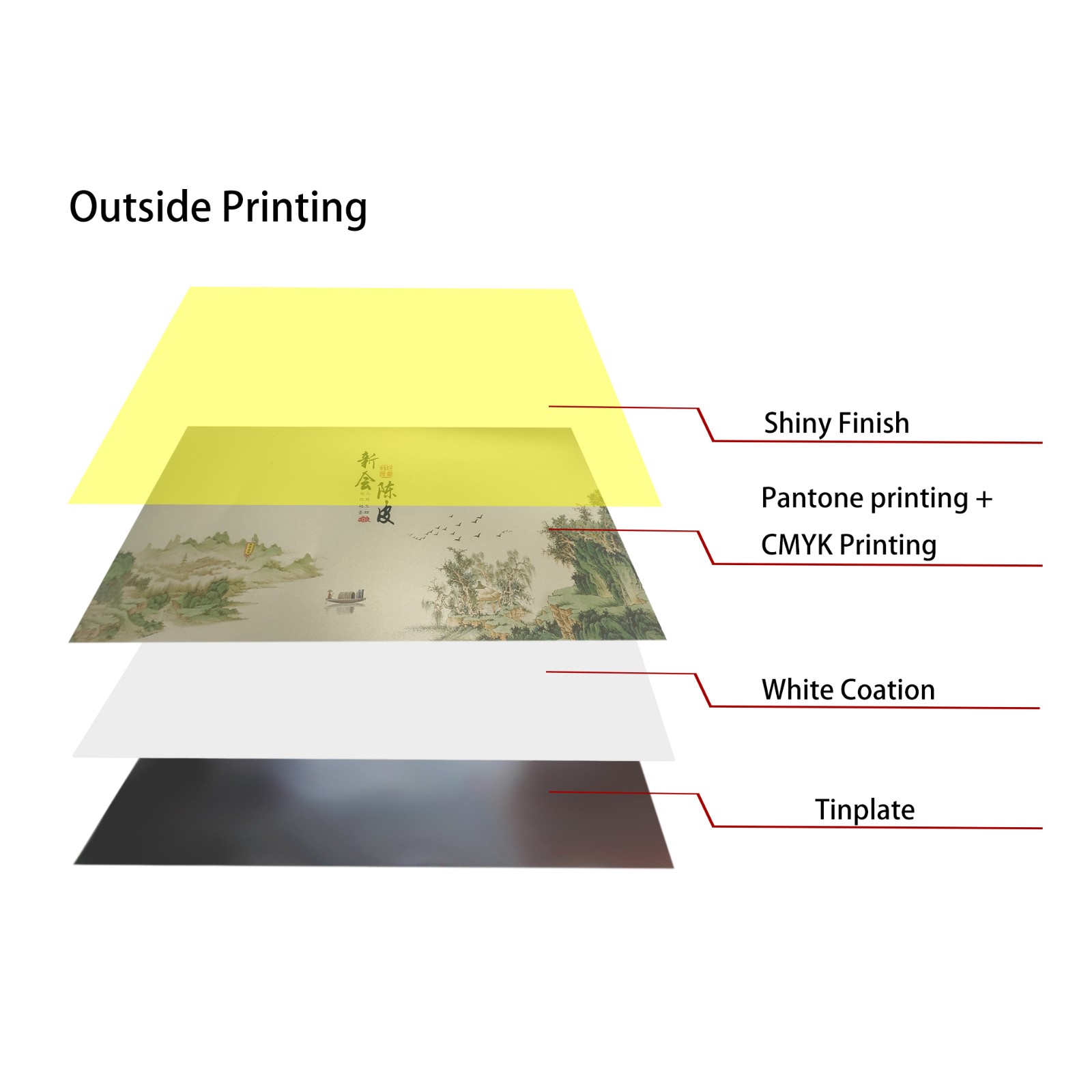
Why is special ink required for tinplate printing?
1. What are the special ingredients of tinplate ink?
Due to the slippery surface of tinplate, ordinary inks have difficulty adhering, so specially designed inks are required. These inks typically contain resins, curing agents, and other ingredients to enhance ink adhesion and scratch resistance. Furthermore, tinplate inks must be heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant to withstand subsequent processing requirements of tinplate products, such as high-temperature baking and pressing. Printing on tinplate sheet using ordinary inks can easily cause the design to peel or discolor, so using specialized inks is crucial to ensuring print quality.
2. How does the ink drying method affect the printing effect?
In tinplate printing, the ink drying method directly affects the printing quality. Common drying methods include natural drying, oven drying, and UV curing. Natural drying, while simple, dries slowly and is prone to smudging. Oven drying uses heat to dry the ink quickly, but requires strict temperature control to prevent metal deformation. UV curing dries the fastest and maintains the clarity and vividness of the design. The drying method should be selected based on the ink type and the desired design to achieve the best printing results.
What are the steps in the tinplate printing process?
1. What does the preparation phase involve?
The first step in tinplate sheet printing is the preparation phase. This phase involves designing the printed pattern and color separation to ensure accurate color reproduction. The pattern is then adjusted to the size and shape of the tinplate sheet to accommodate subsequent can molding. Next, the appropriate ink is selected, the printing equipment is determined, and the tinplate surface is treated to improve ink adhesion and print quality.
2. What details require attention during the printing process?
During the printing process, controlling ink uniformity and color accuracy is crucial. Multiple test prints are typically required to ensure the color, depth, and clarity of the pattern meet standards. Different printing processes require different operational details. For example, offset printing requires precise control of roller pressure to prevent pattern deformation or fading; screen printing requires controlling the angle and force of the squeegee to ensure uniform ink application.
3. How does post-processing ensure the durability of the print?
After printing, tinplate often requires post-processing to enhance the durability of the printed pattern. The most common post-processing steps are baking and spraying a transparent protective lacquer. Baking ensures the ink adheres securely, preventing fading or scratching; the protective lacquer enhances the wear resistance and gloss of the design, making it less susceptible to damage during storage and transportation. The protective lacquer should be applied evenly to avoid run marks or bubbles to ensure consistent printing.
How is tinplate printing quality tested?
1. How is color consistency tested?
Color consistency is a key quality indicator for tinplate sheet printing. During testing, a colorimeter is typically used to measure the color values of each batch of printed products to ensure that color deviations are within acceptable limits. Visual inspection is also essential, especially for prints with gradient colors or complex patterns. Professional inspectors' experience and visual observation ensure color consistency.
2. How is wear and corrosion resistance tested?
The wear and corrosion resistance of printed tinplate products is directly related to their service life, especially for daily necessities packaging that is subject to frequent contact. Abrasion resistance testing typically uses a friction tester to test the pattern's resistance to wear. Corrosion resistance testing involves simulating storage conditions under specific humidity and temperature conditions to observe whether the pattern exhibits discoloration or blistering. Only after passing rigorous abrasion and corrosion resistance testing can printed products be released to the market.
3. Does Adhesion Meet Standards?
Ink adhesion is crucial for ensuring print quality. Testing can be performed using the "cross-cut" or "tape-peel" methods to assess ink adhesion to the tinplate sheet surface. The cross-cut method divides the printed pattern into small squares and then pulls them with tape to see if the ink comes off. The tape-peel method directly applies tape to the surface to see if the ink pulls off. Printed products that meet the required adhesion standards are resistant to fading or peeling, making them suitable for long-term storage and use.

What are the applications of tinplate sheet printing?
1. How can we ensure printing quality on food and beverage cans?
Tinplate printing is widely used in food and beverage packaging. These products require not only clear patterns and vibrant colors but also high corrosion resistance. Food packaging is typically baked or lacquered to prevent fading when exposed to moisture or acid. To ensure food safety, the ink composition must be strictly controlled during the printing process to avoid contamination.
2. Why is tinplate printing so popular for gift packaging?
Tinplate's excellent plasticity and durability, coupled with its wide range of printed designs, make it a popular choice for the gift packaging industry. Exquisite printed designs elevate gift packaging, and processes like silk-screen and UV printing create a three-dimensional effect and gloss. Tinplate sheet printing for gift packaging requires stringent requirements to ensure that the design maintains its original appearance during long-term storage, unaffected by temperature and humidity.
Through these processes and techniques, tinplate sheet printing can achieve exquisite, long-lasting designs, making it widely used in food, beverage, and gift packaging.
How does Dekai manage quality and safety in production?
We implement strict quality control systems at every stage of production. From raw material inspection to final product testing, we use high-end QC equipment and follow ISO9001-certified standards. Our goal is to supply safe, durable, and reliable packaging solutions that meet international requirements. Trust Dekai for consistent quality and worry-free purchasing from China.

