Tinplate sheet is a metal material widely used in food packaging, chemical packaging and other industries. It is a thin steel plate with a tin layer on the surface. Usually, a thin tin layer is covered on the cold-rolled steel plate by electroplating or hot-dip plating, forming a metal material that is corrosion-resistant, wear-resistant and has a certain gloss. This article will introduce the composition and characteristics of tinplate sheet in detail, and focus on its performance under high temperature conditions.

What are the composition and characteristics of tinplate sheet?
Tinplate sheet is a material formed by combining two metals, steel and tin, through a process. Its core component is low-carbon cold-rolled steel plate, and the outside is covered with an extremely thin layer of tin. Steel itself has strong mechanical strength, but it is easy to oxidize and rust, and the main function of tin is to protect the surface of steel from oxidation and corrosion. The tin layer can be combined with the steel plate in a variety of ways, of which electroplating and hot-dip plating are the two main methods. The thickness of the tin layer is usually between a few microns and more than ten microns. Although it is very thin, it provides significant protection for the steel plate.
1. Corrosion resistance
Tin is the most critical anti-corrosion material for tinplate sheet. Because tin has good corrosion resistance, it can isolate oxygen and moisture in the air and prevent steel plates from rusting. Especially in food packaging, tinplate sheet can ensure that food can be stored for a long time without being contaminated by rust problems. At the same time, the surface of tinplate sheet can be coated with other anti-corrosion coatings or printed patterns to further improve its corrosion resistance.
2. Solderability
The solderability of tinplate sheet depends on the thickness of the tin layer and the welding process. In most cases, tinplate sheet will encounter some challenges when welding due to the tin layer on its surface. Tin has a low melting point, so precise temperature control measures need to be taken during welding to avoid excessive melting of the tin layer and affect the welding quality.
3. Formability and processability
Since the core material of tinplate sheet is cold-rolled steel sheet, which has good mechanical strength, ductility and toughness, tinplate sheet can be processed by stamping, bending and other processes to make containers and packaging products of various shapes. These characteristics make tinplate sheet widely used in food packaging, electronic device housings and other fields.
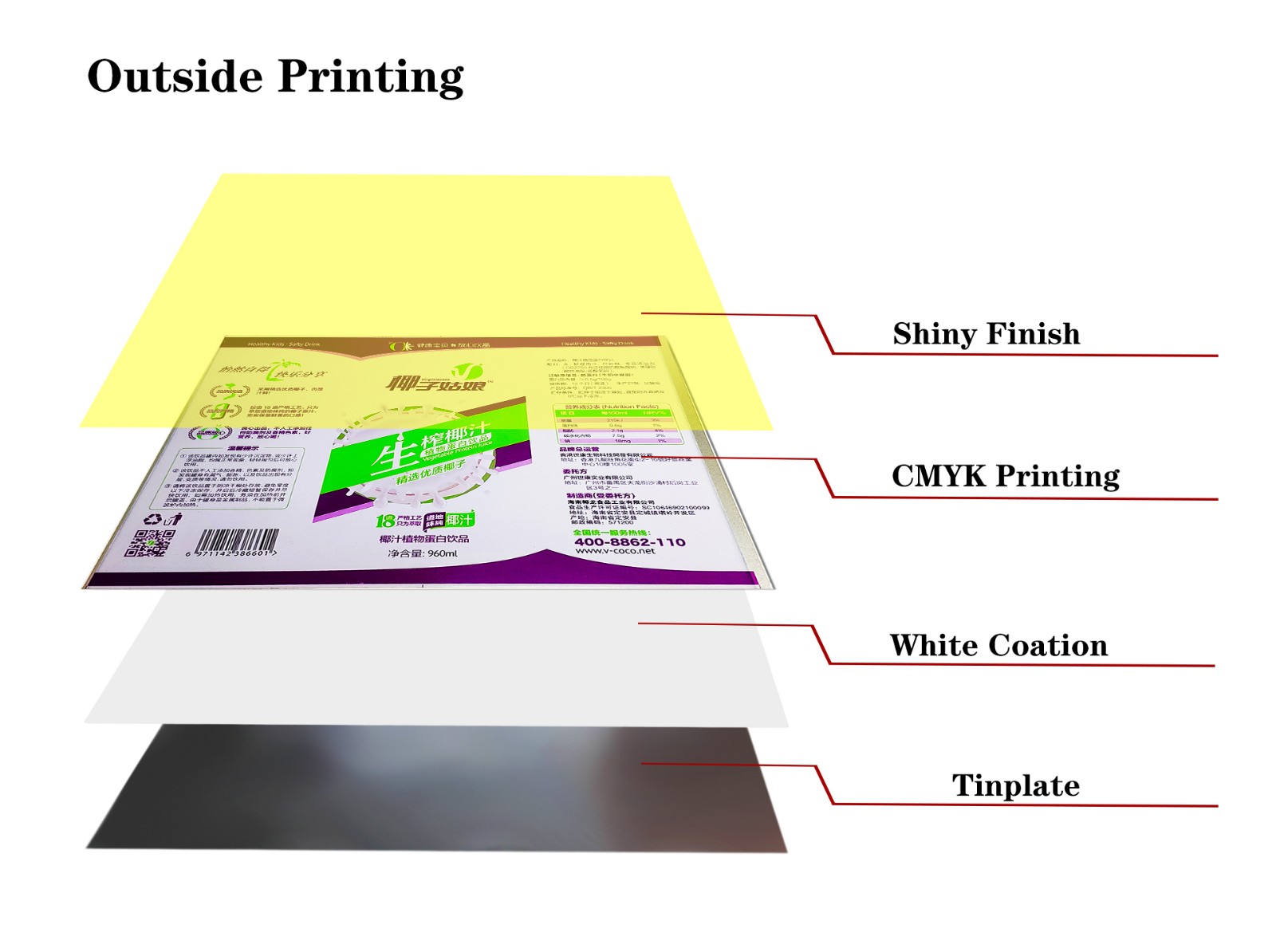
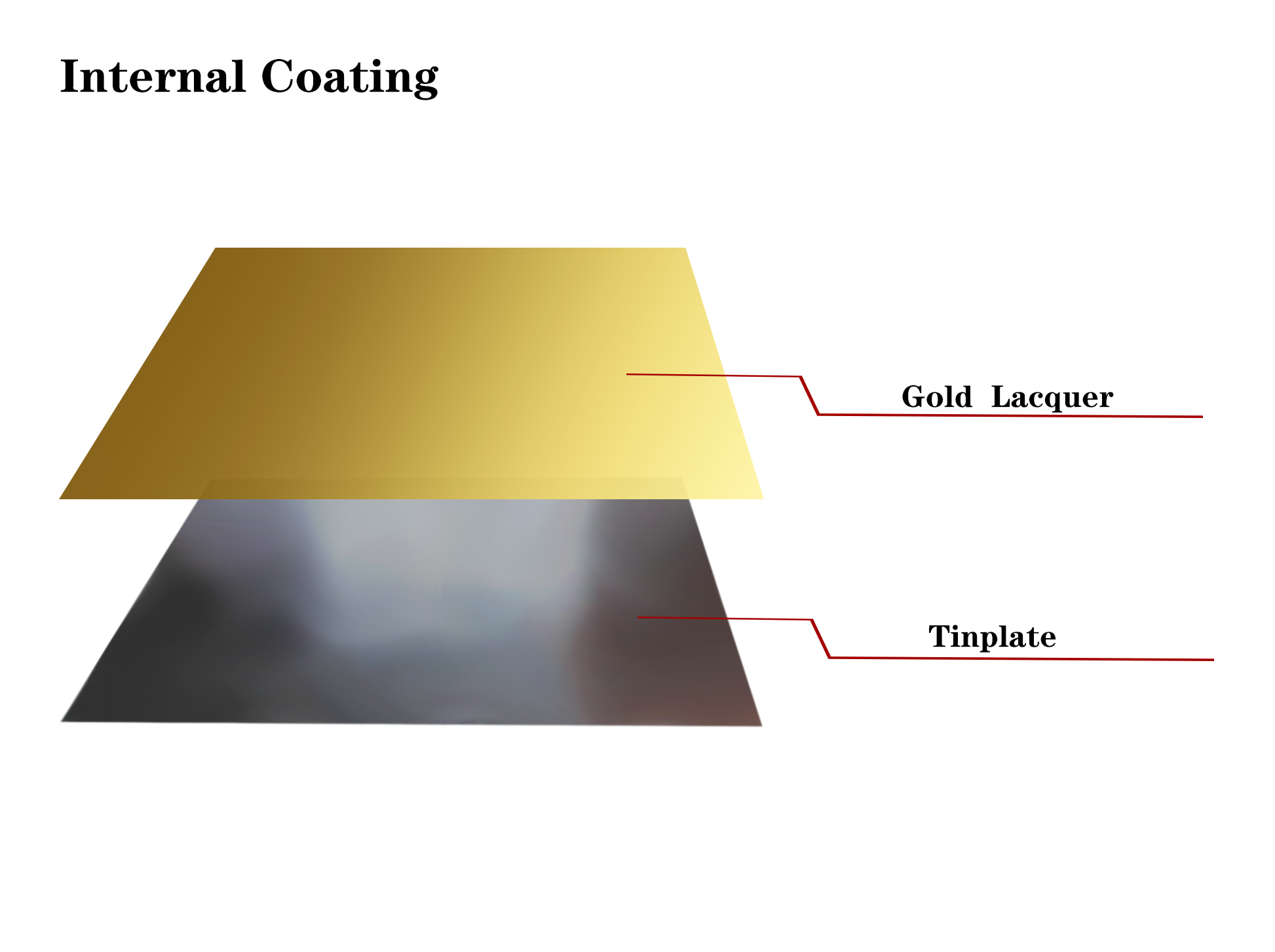
How does tinplate sheet perform under high temperature conditions?
Although tinplate sheet performs well at room temperature, with excellent corrosion resistance and machinability, its performance in high temperature environments is more complicated. High temperature affects the chemical stability of tin and steel and the physical properties of the material, which poses new challenges to the application of tinplate sheet.
1. Melting point of tin and the impact of high temperature
The melting point of tin is relatively low, only about 232°C. When the temperature reaches or exceeds this level, the tin layer on the surface of tinplate sheet will undergo obvious physical changes and may even melt. This phenomenon makes tinplate sheet face greater limitations in high temperature applications. Especially when exposed to high temperature environment for a long time, the protective effect of the tin layer will be significantly reduced or even completely ineffective.
The melting of tin does not only mean that the surface loses its protective layer, but the melted tin may also react chemically with the surrounding materials, causing further oxidation of the steel plate. For example, when tinplate sheet is used in a high temperature environment containing oxygen, the tin layer melts and exposes the surface of the steel plate, and the steel will quickly oxidize to form rust, causing the mechanical properties and appearance of the material to be damaged.
2. Volatilization and diffusion effect of tin
In addition to melting, tin has a certain volatility under high temperature conditions. Although the volatilization rate of tin is slow, it will gradually evaporate from the surface of the steel plate under continuous high temperature, especially in a high temperature environment of more than 400°C, the volatilization rate of tin will be significantly accelerated. The volatilization of tin will cause the tin layer to gradually become thinner, further weakening its protective effect on the steel plate.
In addition, tin is prone to diffusion at high temperatures. Tin atoms will gradually diffuse into the steel plate, causing the interface between the tin layer and the steel plate to become blurred, thereby reducing the protective effect of the tin layer. This diffusion behavior usually occurs at temperatures above 300°C and intensifies with increasing temperature.
3. Performance degradation of steel
The core material of tinplate sheet is low-carbon cold-rolled steel plate, and its performance will also be significantly affected by high temperature. Generally speaking, steel will have problems such as reduced strength and reduced toughness at high temperatures, especially when it exceeds 500°C, the crystal structure of the steel begins to change, resulting in a sharp decline in its mechanical properties.
For tinplate sheet, the degradation of steel at high temperature is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
● Decreased yield strength: As the temperature increases, the yield strength of steel will decrease significantly. This means that in a high temperature environment, the load-bearing capacity of tinplate sheet will be significantly reduced, and it is easy to deform or even break.
● Increased ductility: Although the strength of steel decreases, its ductility increases with the increase of temperature. This makes tinplate sheet more prone to plastic deformation in a high temperature environment, especially under mechanical stress, which may cause the material to fail to maintain its original shape.
● Increased oxidation: As mentioned earlier, when the tin layer fails or falls off in a high temperature environment, the steel plate will be directly exposed to the air, and oxidation reaction will occur rapidly to generate rust. Oxidation will further weaken the strength of the steel and accelerate the failure of the material.
4. Heat treatment reaction of tinplate sheet
In some industrial applications, tinplate sheet may undergo a certain heat treatment process. During the heat treatment process, the physical and chemical properties of tinplate sheet will change. For the tin-plated layer, heat treatment usually causes diffusion at the bonding interface between the tin layer and the steel plate, which in turn affects its protective effect. At the same time, high temperature may cause the internal lattice of the steel sheet to rearrange, thus affecting its mechanical properties.
Especially under high temperature tempering treatment, the hardness and strength of the steel will change, resulting in fluctuations in the overall mechanical properties of the tinplate sheet. Although heat treatment is necessary in some cases, improper high temperature treatment may cause the tinplate sheet to lose its original protective and structural properties.
5. High temperature stability of coatings and printing
In order to enhance the protective ability and aesthetics of tinplate sheet, the surface of many tinplate sheet products is covered with an anti-corrosion coating or printed pattern. These coatings and patterns are usually composed of polymers or other organic substances, which have good stability and corrosion resistance at room temperature.
However, the high temperature resistance of coatings and printed materials is generally poor. Generally speaking, the heat resistance temperature of most organic coatings and inks is between 150°C and 200°C. After exceeding this temperature, they may soften, melt, discolor or decompose. This will not only affect the appearance of tinplate sheet products, but also lead to a decrease in their protective effect.
Why Choose Foshan Dekai for Metal Packaging?
At Foshan Dekai Metal Packaging Co., Ltd., we understand that quality and price are key factors in your purchasing decisions. That’s why we offer a wide range of metal packaging products, including aerosol cans and custom-printed tinplates, all manufactured with precision using advanced machinery. Our factory is ISO 9001 certified, ensuring every product meets international quality standards. We provide low-price solutions without compromising on quality, and our efficient production lines guarantee quick turnaround times.

